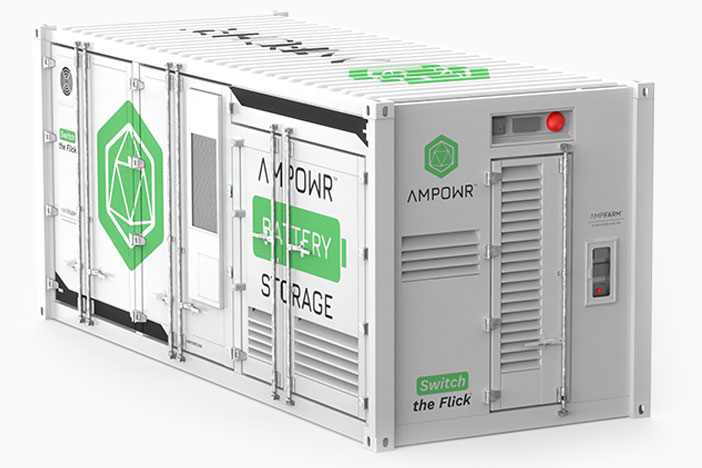
GRID CONGESTION: CAUSES, IMPACT, AND SOLUTIONS (battery energy storage system)
What is grid congestion?
Grid congestion is a critical issue in the modern electrical grid systems, impacting energy distribution and business operations worldwide. This article delves into the concept of grid congestion, its causes, the countries most affected, with a particular focus on the Netherlands, its impact on businesses, future consequences, and potential solutions with an emphasis on Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS).
Addressing grid congestion
Grid congestion can have wide-ranging impacts on countries, affecting not only the reliability and affordability of electricity supply but also economic productivity, consumer welfare, and the transition to cleaner energy sources. Addressing grid congestion requires strategic investments in infrastructure upgrades, demand management, and innovative grid technologies to enhance the flexibility and resilience of the electrical grid.
HOW IS GRID CONGESTION?
Grid congestion occurs when the demand for electricity in a particular area exceeds the capacity of the transmission infrastructure to deliver it efficiently. This imbalance leads to an overloaded grid, causing inefficiencies and potential blackouts. Essentially, grid congestion is the “traffic jam” of the electricity grid, where the infrastructure can’t handle the volume of electricity being transported. Grid congestion is primarily a result of the following factors:
Increased demand
Rapid urbanization and industrial growth lead to higher electricity consumption, which can surpass the existing grid capacity.
Generation disparities
The location of power generation (e.g., renewable energy sources like wind farms) may be far from consumption centers, requiring extensive transmission.
Aging infrastructure
Outdated transmission lines and equipment struggle to handle modern electricity loads.
Renewable energy integration
The intermittent nature of renewable energy sources like solar and wind can create fluctuations in supply, leading to congestion.
Regulatory and planning issues
Inadequate planning and slow regulatory responses can hinder grid upgrades and expansions necessary to prevent congestion.
The core function of energy storage systems for wind turbines is to capture and store the excess electricity. These systems typically incorporate advanced battery technologies, such as lithium-ion batteries, to efficiently store the energy for later use. During times of high wind production, the excess electricity charges the batteries, allowing them to store the energy in a stable and reliable manner. When needed, the stored energy is discharged from the batteries, providing a consistent power source that complements the wind turbine’s electricity production.


Impact of grid congestion on business
Disrupted Operations
Grid congestion can lead to power outages or voltage fluctuations, disrupting business operations. This can result in production delays, reduced productivity, and potential damage to equipment, particularly in industries reliant on continuous power supply such as manufacturing, data centers, and healthcare facilities.
Financial Losses
Businesses may incur significant financial losses due to interrupted operations, missed deadlines, and damaged equipment. These losses can include direct costs associated with downtime, as well as indirect costs such as lost sales, damaged reputation, and potential contractual penalties.
Increased Costs: Grid congestion may force businesses to rely on alternative, more expensive sources of power during peak demand periods. Additionally, businesses may need to invest in backup power systems or energy storage solutions to mitigate the impact of outages, leading to increased operational costs.
Supply Chain Disruptions
Businesses reliant on just-in-time manufacturing or logistics may face disruptions in their supply chains due to grid congestion-related power outages. This can lead to delays in receiving raw materials or delivering finished products, impacting customer satisfaction and competitiveness.
Investment Uncertainty
Grid congestion can create uncertainty for businesses considering investments in new facilities or expansions. Concerns about the reliability and stability of the electrical grid may deter companies from locating or expanding operations in areas prone to grid congestion, affecting economic growth and employment opportunities.
How energy management systems can mitigate the effects of grid congestion?
Energy management systems (EMS) are instrumental in tackling grid congestion by optimizing energy usage and enhancing grid stability. They achieve this by facilitating load shifting, integrating distributed energy resources, and implementing demand response programs. Through load shifting, EMS encourages consumers to adjust their energy consumption during peak hours, alleviating strain on the grid. By integrating DERs like solar panels and batteries, EMS reduces dependency on centralized energy sources, easing congestion on transmission lines.
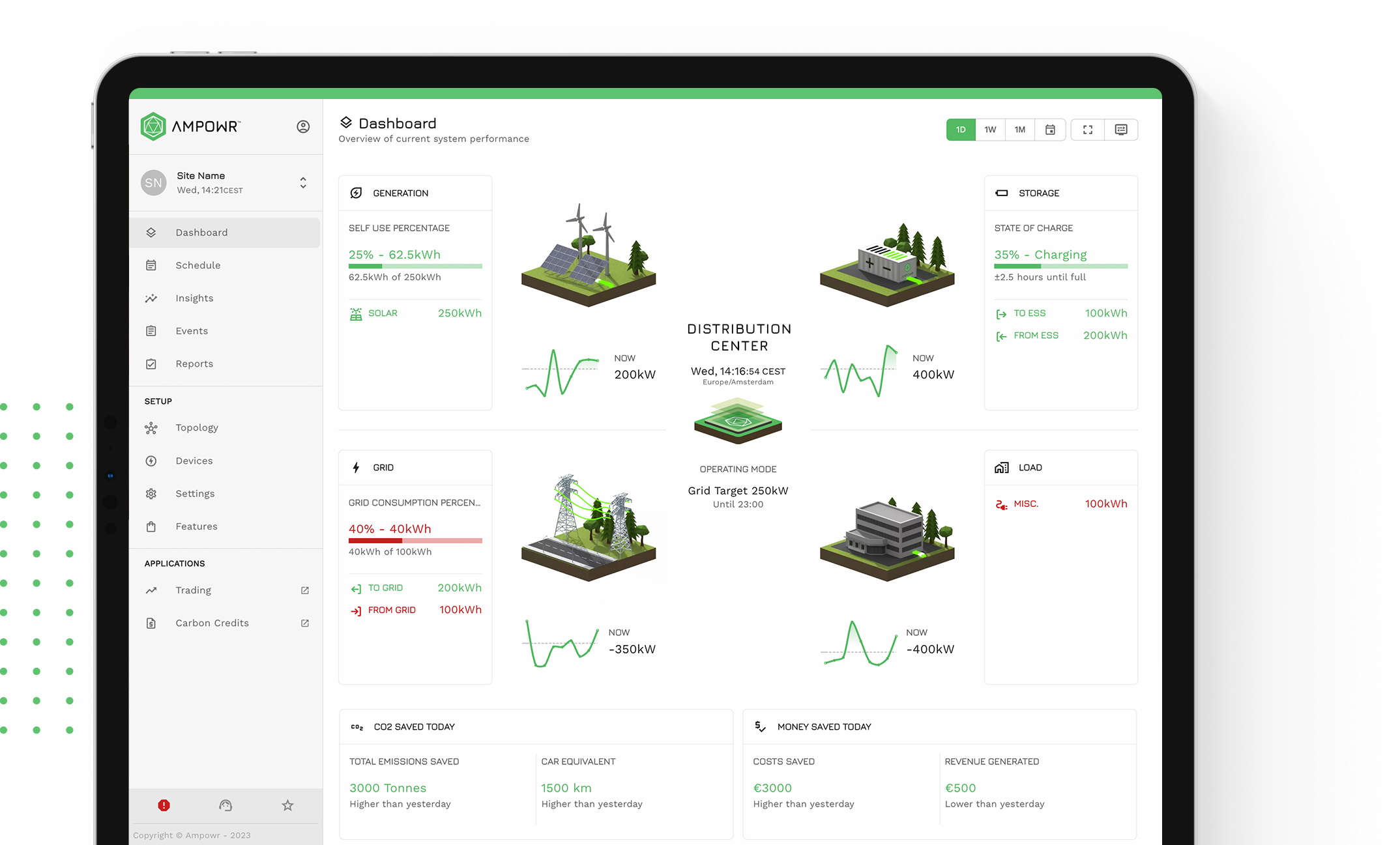
Additionally, EMS enables utilities to remotely control energy consumption, engaging in load shedding during congestion events. By dynamically adjusting voltage levels and optimizing energy flow, EMS minimizes bottlenecks and enhances grid efficiency. Moreover, EMS provides insights into grid performance, aiding in strategic grid expansion planning to mitigate congestion risks.
Through market mechanisms and predictive analytics, EMS promotes efficient resource allocation and proactive congestion management. Overall, EMS plays a pivotal role in ensuring grid reliability and efficiency amidst growing energy demands and congestion challenges.
Grid Congestion Solutions: battery energy storage systems
Our Smart Battery Energy Storage Systems are leading the energy transition and powering a wide range of industries and applications.





